The Black Prince’s great victory on 19th September 1356 in the Hundred Years War over the French King John II
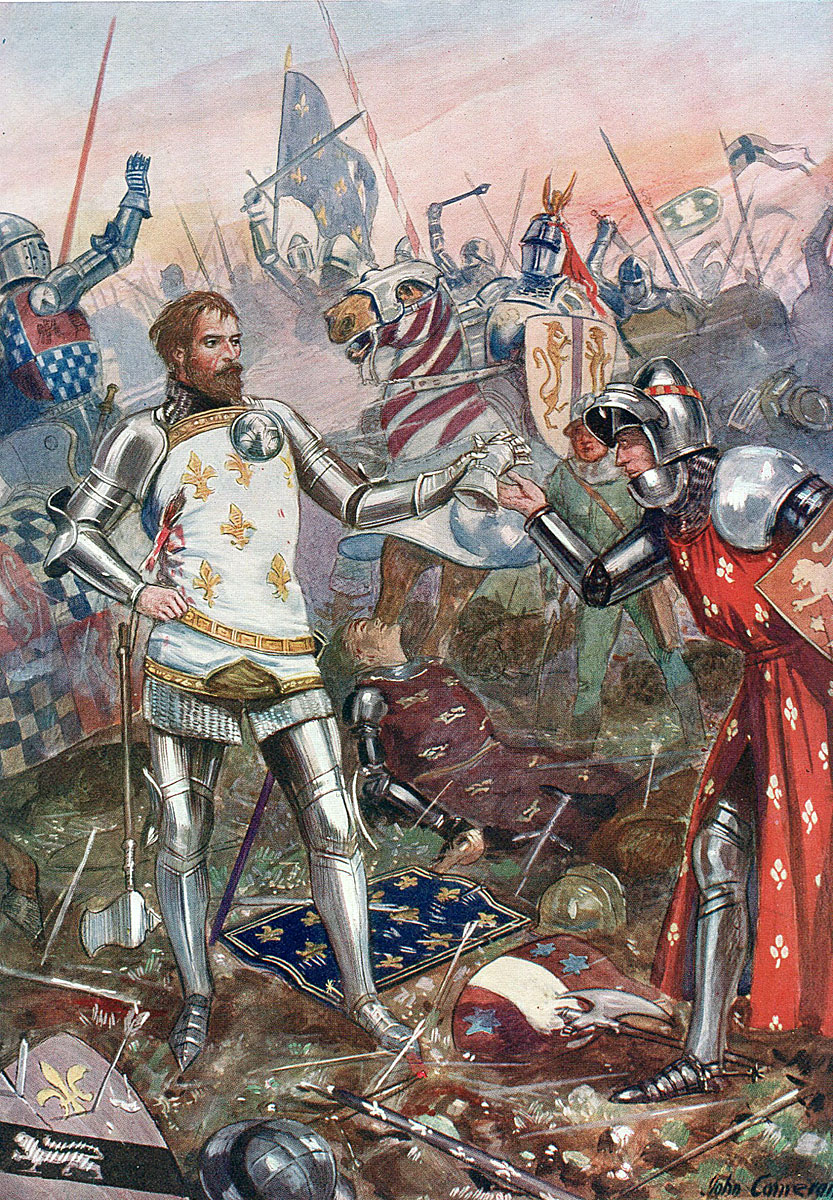

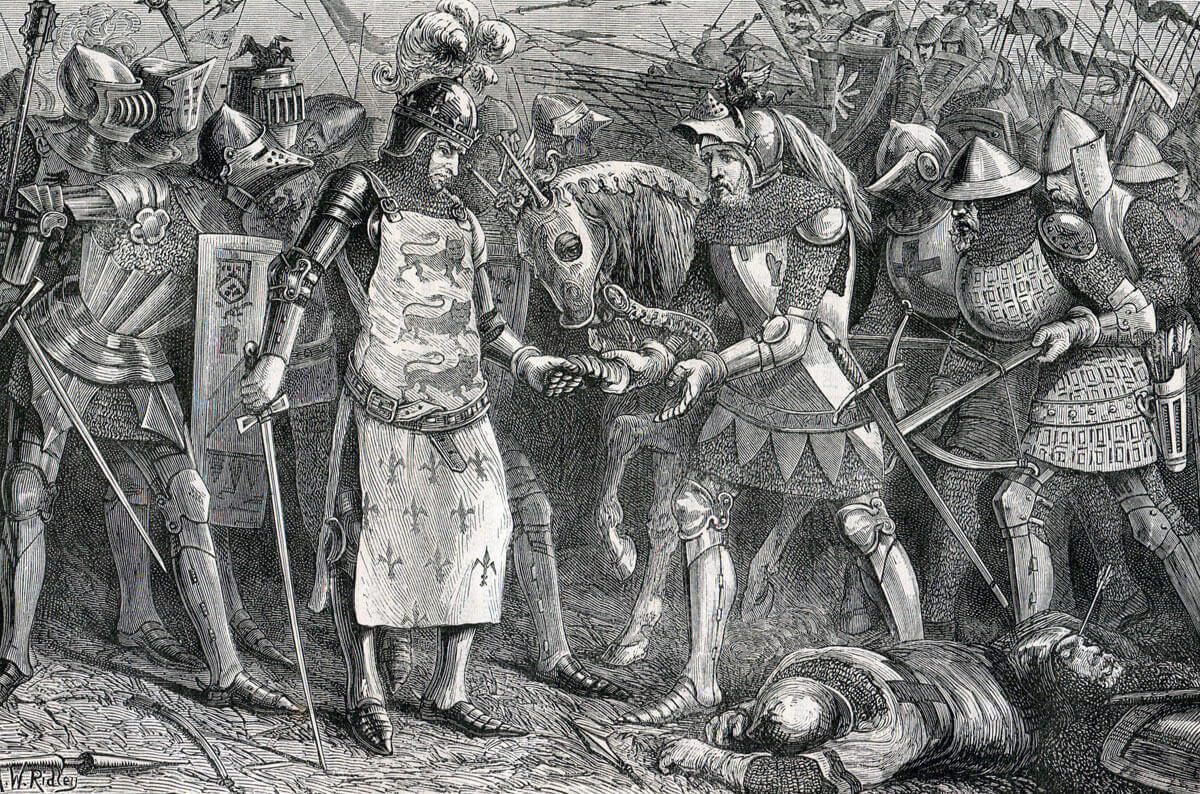
King John II of France surrendering himself to the English at the Battle of Poitiers on 19th September 1356 in the Hundred Years War
The previous battle of the Hundred Years War is the Battle of Mauron
The next battle of the Hundred Years War is the Battle of Cocherel
War: Hundred Years War
Date of the Battle of Poitiers: 19th September 1356.
Place of the Battle of Poitiers: Western France.
Combatants at the Battle of Poitiers: An army of English and Gascons against the French and their allies.
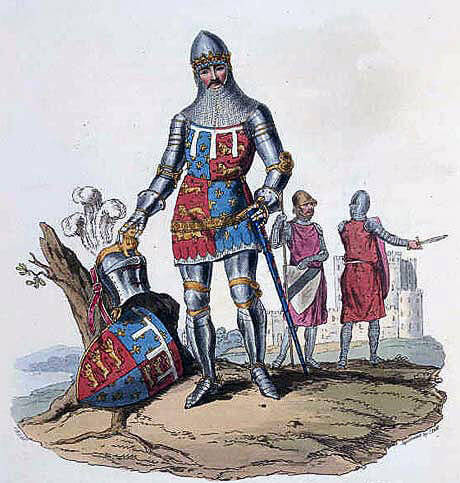

Edward, the Black Prince, commander of the English army at the Battle of Poitiers on 19th September 1356 in the Hundred Years
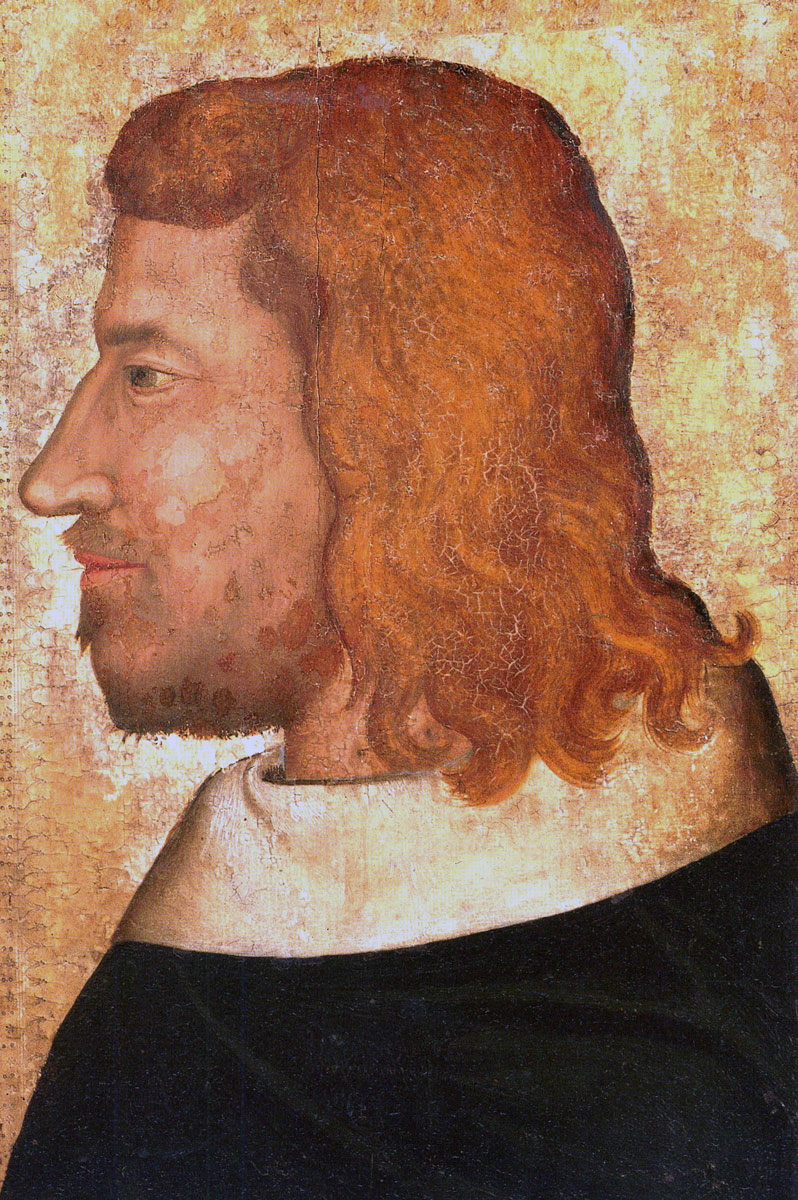
Commanders at the Battle of Poitiers: The Black Prince against King John II of France.
Size of the armies at the Battle of Poitiers: The Black Prince’s army numbered some 7,000 knights, men-at-arms and archers.
Numbers in the French army are uncertain but were probably around 35,000, although Froissart gives the size of the French army as 60,000. The French army comprised a contingent of Scots commanded by Sir William Douglas.
Uniforms, arms and equipment in the Battle of Poitiers: Depending upon wealth and rank a mounted knight of the period wore jointed steel plate armour incorporating back and breast plates, a visored bascinet helmet and steel plated gauntlets with spikes on the back, the legs and feet protected by steel greaves and boots, called jambs. Weapons carried were a lance, shield, sword and dagger. Over the armour a knight wore a jupon or surcoat emblazoned with his arms and an ornate girdle.
The weapon of the English and Welsh archers was a six foot yew bow discharging a feathered arrow of a cloth yard. The rate of fire was up to an arrow every 5 seconds. For close quarter fighting the archers used hammers or daggers.
Winner of the Battle of Poitiers: The English and Gascons decisively won the battle.
Account of the Battle of Poitiers: Edward III, King of England, began the Hundred Years War, claiming the throne of France on the death of King Philip IV in 1337. The war finally ended in the middle of the 15th Century with the eviction of the English from France, other than Calais, and the formal abandonment by the English monarchs of their claims to French territory.
The war began well for Edward III with the decisive English victories at Sluys in 1340 and Creçy in 1346 and the capture of Calais in 1347. In the late 1340s the plague epidemic, called the Black Death, decimated the populations of France and England, bringing military operations to a halt; one of the plague’s victims being the French king Philip VI.
In 1355 King Edward III again planned for an invasion of France. His son, Edward the Black Prince, now an experienced soldier 26 years of age, landed at Bordeaux in Western France and led his army on a march through Southern France to Carcassonne. Unable to take the walled city, the Black Prince returned to Bordeaux. In early 1356 the Duke of Lancaster landed with a second force in Normandy and began to advance south. Edward III was engaged in fighting in Scotland.
The new king of France, John II, led an army against Lancaster forcing him to withdraw towards the coast. King John then turned to attack the Black Prince, who was advancing north east towards the Loire pillaging the countryside as he went.
In early September 1356 King John reached the Loire with his large army, just as the Black Prince turned back towards Bordeaux. The French army marched hard and overtook the unsuspecting English force at Poitiers on Sunday 18th September 1356.
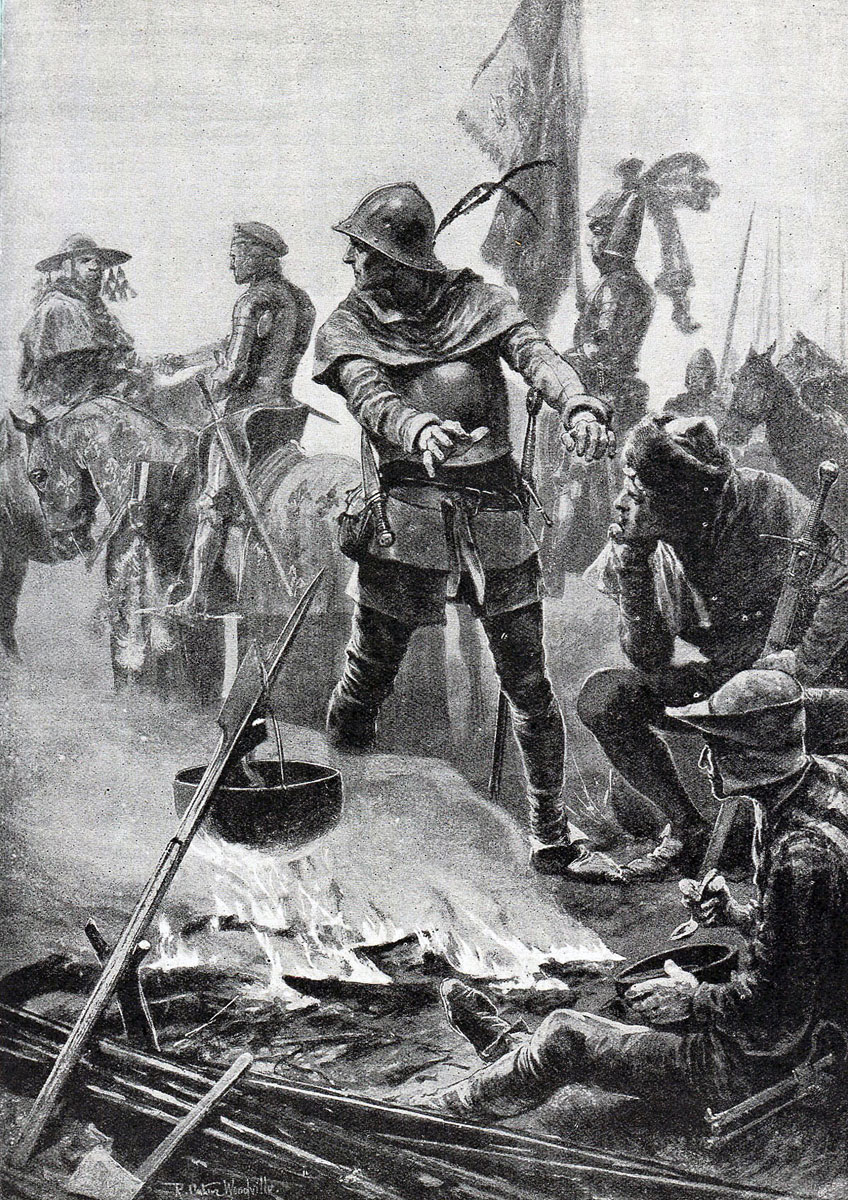

Cardinal Talleyrand leaves the English camp the night before the Battle of Poitiers on 19th September 1356 in the Hundred Years: picture by Richard Caton Woodville
The local prelate, Cardinal Talleyrand de Périgord, attempted to broker terms of settlement between the two armies; but the Black Prince’s offer of handing over all the booty he had taken on his “chevauchée” and maintaining a truce for 7 years was unacceptable to King John who considered the English would have little chance against his overwhelming army, and the French demand that the Black Prince surrender himself and his army was unacceptable to the English. The two armies prepared for battle.
The English army was an experienced force; many of the archers veterans of Creçy, ten years before, and the Gascon men-at-arms commanded by Sir John Chandos, Sir James Audley and Captal de Buche, all old soldiers.
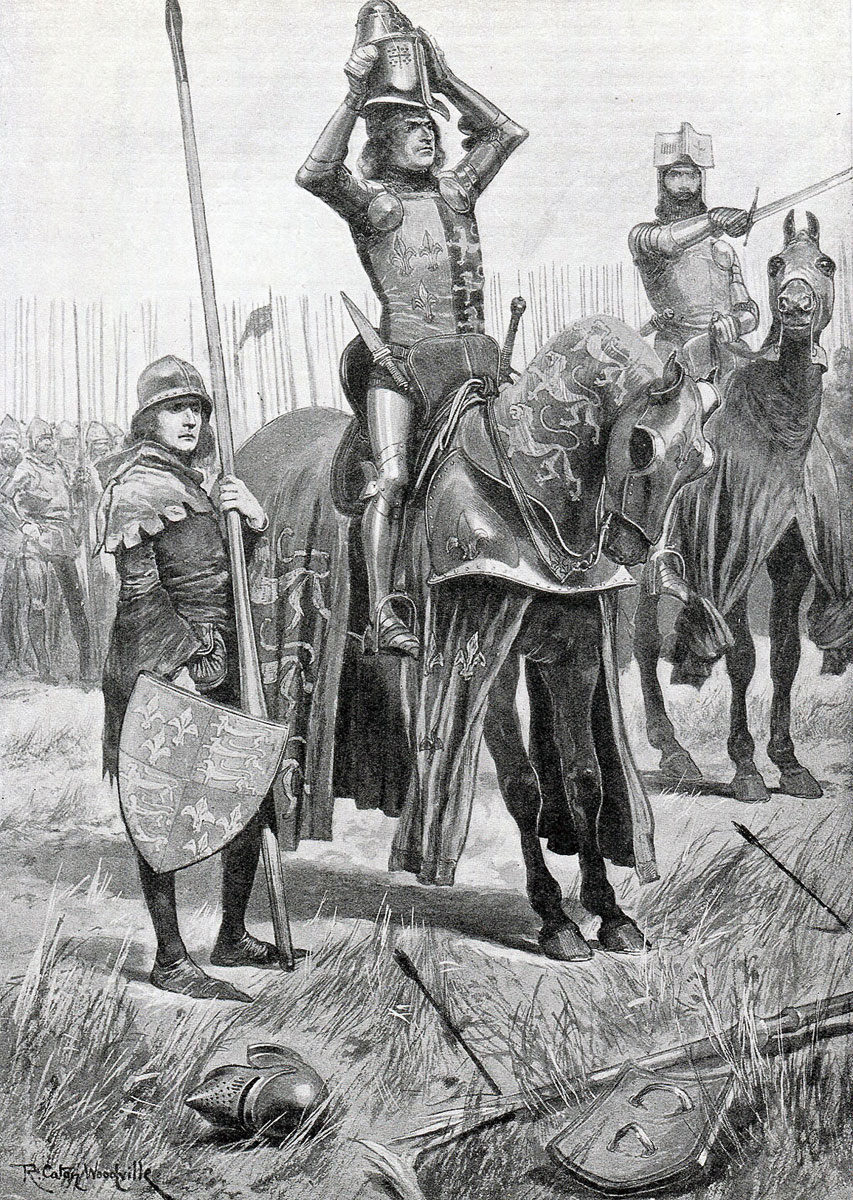

Sir John Chandos urges the Black Prince to attack saying ‘Sire the Day is yours’ at the Battle of Poitiers on 19th September 1356 in the Hundred Years: picture by Richard Caton Woodville
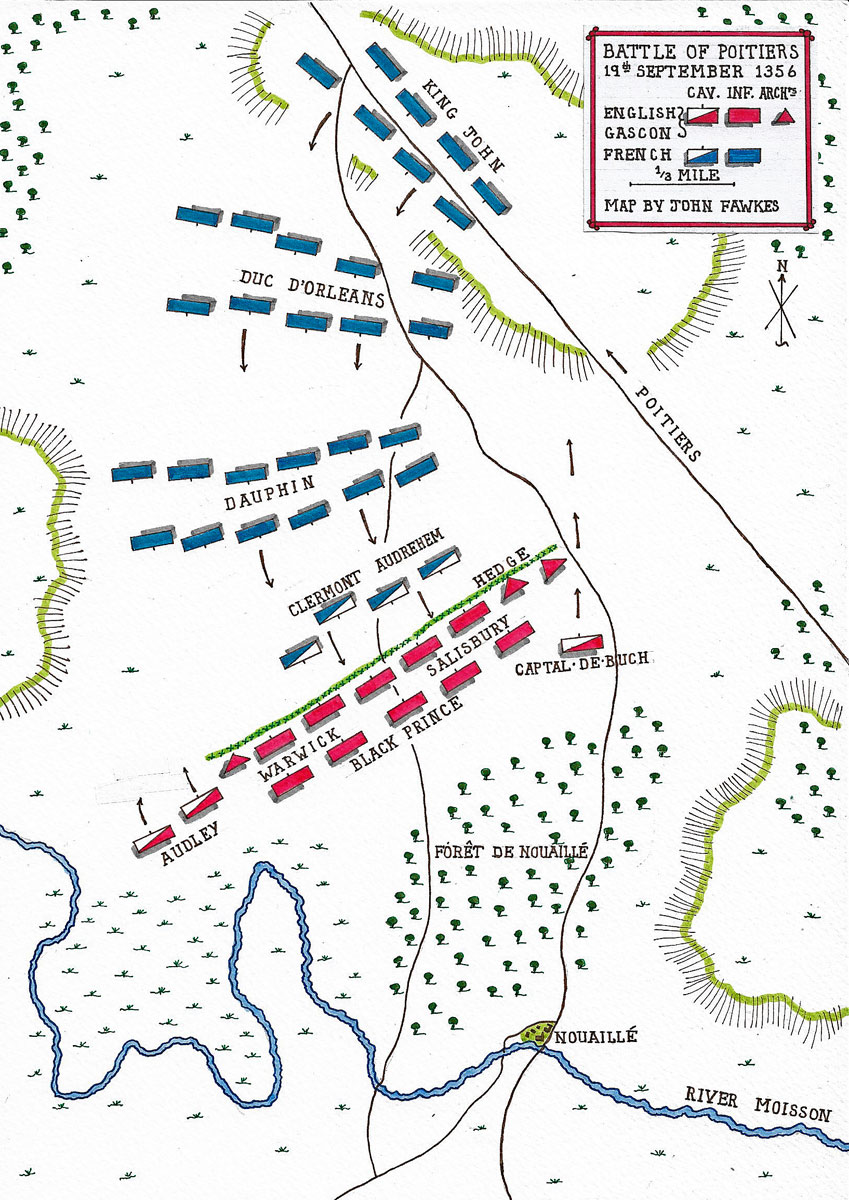
The Black Prince arranged his force in a defensive position among the hedges and orchards of the area, his front line of archers disposed behind a particularly prominent thick hedge through which the road ran at right angles.
King John was advised by his Scottish commander, Sir William Douglas, that the French attack should be delivered on foot, horses being particularly vulnerable to English archery, the arrows fired with a high trajectory falling on the unprotected necks and backs of the mounts. King John took this advice, his army in the main leaving its horses with the baggage and forming up on foot.
The French attack began in the early morning of Monday 19th September 1356 with a mounted charge by a forlorn hope of 300 German knights commanded by two Marshals of France; Barons Clermont and Audrehem. The force reached a gallop, closing in to charge down the road into the centre of the English position. The attack was a disaster, with those knights not shot down by the English archers dragged from their horses and killed or secured as prisoners for later ransom.
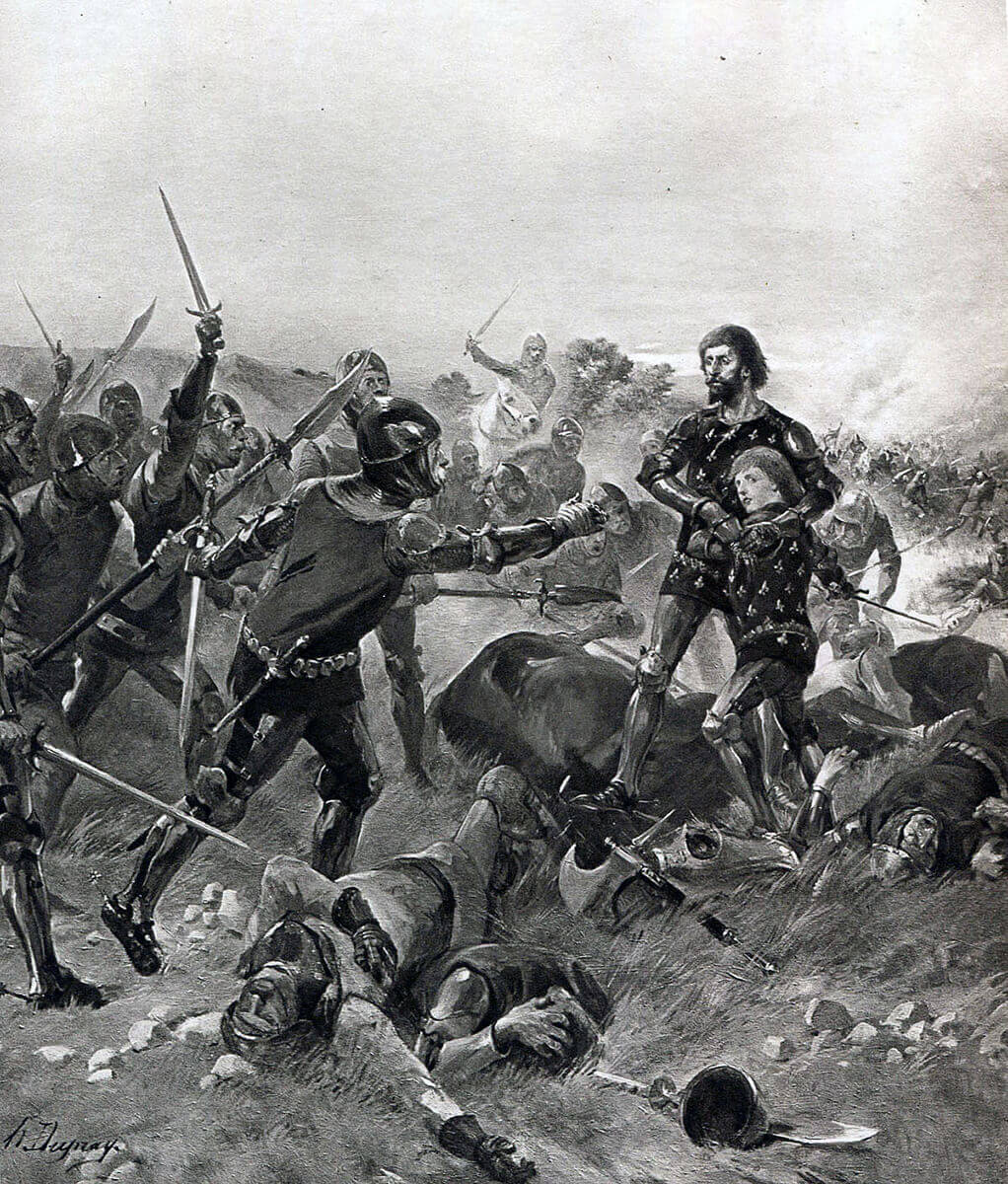

Capture of King John of France and his 14 year old son at the Battle of Poitiers on 19th September 1356 in the Hundred Years: picture by Henri Dupray
The rest of the French army now began its ponderous advance on foot, in accordance with Douglas’ advice, arrayed in three divisions; the first led by the Dauphin Charles (the son of the King), the second by the Duc D’Orleans and the third, the largest, by the King himself.
The first division reached the English line exhausted by its long march in heavy equipment, much harassed by the arrow fire of the English archers. The Black Prince’s soldiers, Gascon men-at-arms and English and Welsh archers, rushed forward to engage the French, pushing through the hedgerow and spilling round the flanks to attack the French in the rear.
After a short savage fight the Dauphin’s division broke and retreated, blundering into the division of the Duc D’Orleans marching up behind, both divisions falling back in confusion.
The final division of the French army, commanded by the king himself, was the strongest and best controlled. The three divisions coalesced and resumed the advance against the English, a formidable mass of walking knights and men-at-arms.
Thinking that the retreat of the first two divisions marked the end of the battle, the Black Prince had ordered a force of knights commanded by the Gascon, Captal de Buche, to mount and pursue the French. Chandos urged the Prince to launch this mounted force on the main body of the French army. The Black Prince seized on Chandos’ idea and ordered all the knights and men-at-arms to mount for the charge. The horses were ordered up from the rear; in the meantime Captal de Buch’s men, already mounted, were ordered to advance around the French flank to the right.

Capture of King John II of France and his 14 year old son at the Battle of Poitiers on 19th September 1356 in the Hundred Years
As the French army toiled up to the hedgerow the English force broke through the hedge and struck the French like a thunderbolt, the impetus of the charge taking the mounted knights and men-at-arms right into the French line. Simultaneously Captal de Buch’s Gascons charged in on the French flank. The English and Welsh archers left their bows and ran forward to join the fight, brandishing their daggers and fighting hammers.
The French army broke up, many leaving the field, while the more stalwart knights fought hard in isolated groups. A mass of fugitives made for Poitiers pursued by the mounted Gascons to be slaughtered outside the closed city gates.
King John found himself alone with his 14 years old younger son Philip fighting an overwhelming force of Gascons and English. Eventually the king agreed to surrender.
The battle won, the English army gave itself up to pillaging the vanquished French knights and the lavish French camp.
Casualties at the Battle of Poitiers: In his dispatch to King Edward III, his father, the Black Prince stated that the French dead amounted to 3,000 while only 40 of his troops had been killed. It is likely that the English casualties were higher. Among the French prisoners were King John II, his son Philip, 17 great lords, 13 counts, 5 viscounts and a hundred other knights of significance.
Follow-up to the Battle of Poitiers: On the night of the battle the Black Prince entertained the King of France and his son to dinner and the next day the English army resumed its march to Bordeaux.
The effect of the defeat on France and the loss of the King to captivity was devastating, leaving the country in the hands of the Dauphin Charles, escaped from the ruins of his division at Poitiers. Charles faced immediate revolts across the kingdom as he attempted to raise money to continue the war and ransom his father.
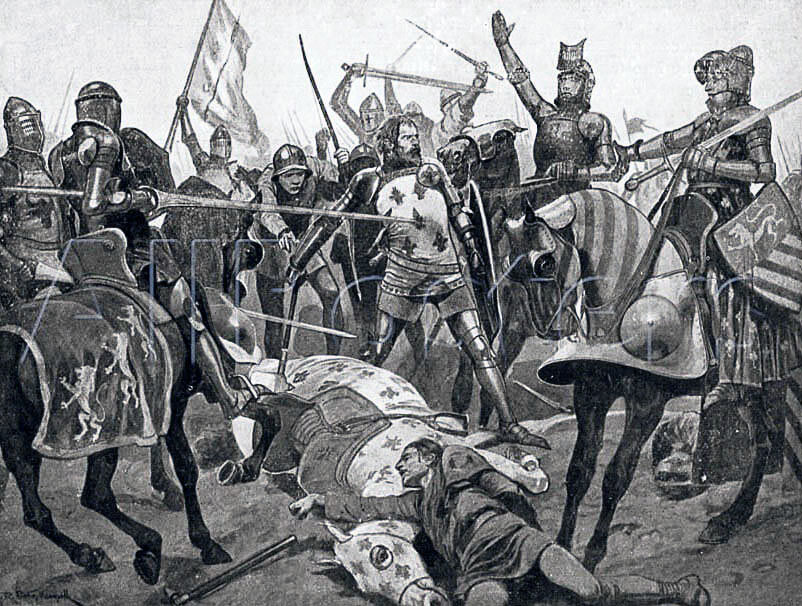

Capture of King John II of France at the Battle of Poitiers on 19th September 1356 in the Hundred Years: picture by Richard Caton Woodville
The release of King John proved difficult to negotiate as Edward III sought to extract more and more onerous terms from the French. Meanwhile the war continued to the misery of the wretched inhabitants of France.
King John was released in November 1361 against other hostages. Due to the default of one of those hostages John returned to London and died there in 1364.
Anecdotes and traditions of the Battle of Poitiers:
- King John actually surrendered to a French knight, Sir Denis de Morbeque, who took him to the Prince of Wales with the Earl of Warwick.
- Poitiers was the second great battle won by the English yew bow, although in this case it was the threat of the arrow barrage that caused the French to launch the ill-judged advance on foot thereby exposing them to the English/Gascon mounted charge that won the battle.
References for the Battle of Poitiers:
The Hundred Years War by Alfred H. Burne
Trial by Fire, Volume lI of the four volume record of the Hundred Years War by Jonathan Sumption.
The Art of War in the Middle Ages Volume Two by Sir Charles Oman
The Hundred Years War by Robin Neillands.
British Battles by Grant.
The previous battle of the Hundred Years War is the Battle of Mauron
The next battle of the Hundred Years War is the Battle of Cocherel